How to Boost Your Wi-Fi Signal: 12 Tips to Improve Wi-Fi Speed
From home users to business professionals, we all want to boost Wi-Fi performance. And why wouldn’t you? Enhanced Wi-Fi performance means better quality of video streams, voice calls, and marathon gaming sessions.
If you’re looking for a way to extend, strengthen, or speed up your existing Wi-Fi and boost Wi-Fi performance, you’re in the right place! In this piece, we’ll explore 12 tips that cover how to boost Wi-Fi signal.
#1: Optimize the Position of Your Wi-Fi Source

You will see many articles online promoting the benefits of placing your Wi-Fi router in a central location. This is a good tip if you are trying to determine how to increase Wi-Fi signal across a home or business that has Wi-Fi clients spread evenly across the premises.
This is a good rule of thumb. However, if most of your Wi-Fi clients are in one area (such as the waiting area of a doctor’s office or a living room full of smart devices), it makes more sense to place your Wi-Fi router there.
Pro Tips
- If your Wi-Fi clients are spread out evenly across the premises, place your Wi-Fi source in the center.
- If your Wi-Fi clients are clustered in a single area, place your Wi-Fi source there.
#2: Use a Wi-Fi Signal Booster
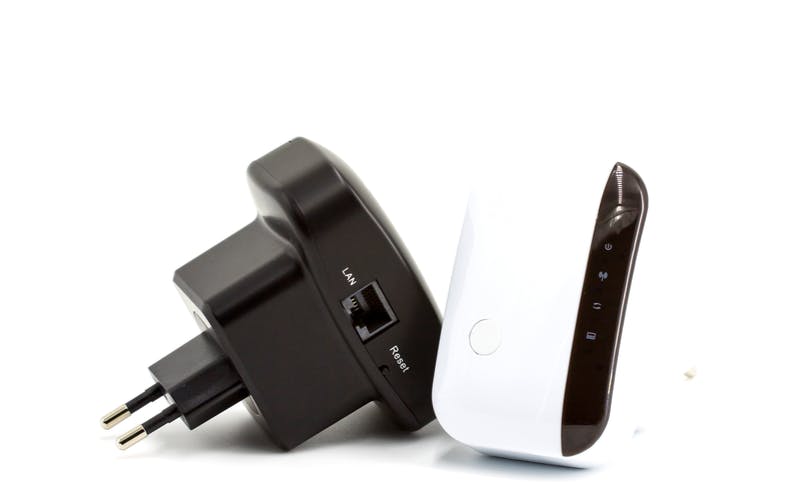

Wi-Fi signal boosters work by amplifying your existing Wi-Fi signal. These signal boosters are useful when addressing Wi-Fi coverage “dead spots”.
Wi-Fi signal boosters fall into two categories: Wi-Fi extenders and Wi-Fi repeaters.
- Wi-Fi repeaters- take in the existing Wi-Fi signal and retransmit it at the same strength. This is a way to boost Wi-Fi signal, but also adds latency to the connection.
- Wi-Fi extenders- operate in a similar fashion as Wi-Fi repeaters, but retransmit the Wi-Fi signal on a different channel. This can help reduce some of the latency effects associated with using a Wi-Fi repeater.
Pro Tips
- The position of your Wi-Fi signal booster is essential. Work to optimize the position of your booster relative to your Wi-Fi source and Wi-Fi clients.
- Pay attention to specifications when looking for the right device for your needs. The industry has not agreed on universal definitions for “Wi-Fi extender” vs. “Wi-Fi repeater”. Using our definitions: a single-band Wi-Fi booster is likely a repeater, while a dual-band device that creates a new SSID (service set identifier or network name) is likely an extender. All else equal, dual-band boosters will have better performance.
#3: Upgrade Your Wi-Fi Router

Wi-Fi standards can be hard to keep up with. Until recently, identifying different Wi-Fi speeds and frequencies required decoding different 802.11 standards. Fortunately, with the release of Wi-Fi 6 (a.k.a. 802.11ax) Wi-Fi versions are being categorized into easy to understand numerical versions (Wi-Fi 1, Wi-Fi 2, etc.). A higher Wi-Fi generally implies better maximum Wi-Fi speed and performance. Of course, your Wi-Fi client devices need to support the upgraded Wi-Fi versions to experience benefits.
Today, you’re likely to be looking at Wi-Fi routers that support one or more of these standards:
- Wi-Fi 4 (802.11n)- Released in 2009, it supports theoretical speeds of up to 300 Mbps (Megabits per second), 2.4 GHz (Gigahertz) & 5 GHz bands.
- Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac)- Officially released in 2014, Wi-Fi 5 supports maximum theoretical speeds of 1.3 Gbps (Gigabits per second) and 2.4 GHz & 5 GHz bands.
- Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax)- Released in 2019 Wi-Fi 6 is designed to support dense Wi-Fi environments and can deliver a max speed upwards of 10 Gbps. It also supports 2.4 GHz & 5 GHz bands.
Pro Tips
- If you currently have a Wi-Fi router that only supports older standards like 802.11g, 802.11b, or 802.11a, you’ll almost certainly see a Wi-Fi performance boost if you upgrade your router to one that supports a more modern protocol.
- If you already have at least Wi-Fi 4 equipment in your network, evaluate your usage to determine if a Wi-Fi router upgrade is warranted.
- Wi-Fi 5 is still sufficient for most home and small business applications.
A note on max Wi-Fi speeds: as demonstrated in this Wi-Fi 6 article from The Verge, there isn’t really a hard and fast answer when it comes to max Wi-Fi speeds. Keep that in mind when reviewing Wi-Fi specifications.
#4: Upgrade Your PC Hardware

The Wi-Fi adapter on your PC can lead to slow Wi-Fi speeds much in the same way an old router can. Fortunately, you don’t have to buy a new PC to boost Wi-Fi performance. You can get your PC up to speed by adding a new Wi-Fi network interface card that supports a modern Wi-Fi protocol. Many USB Wi-Fi adapters exist that make the process of updating your PC’s wireless hardware as simple as connecting a USB dongle.
Pro Tip
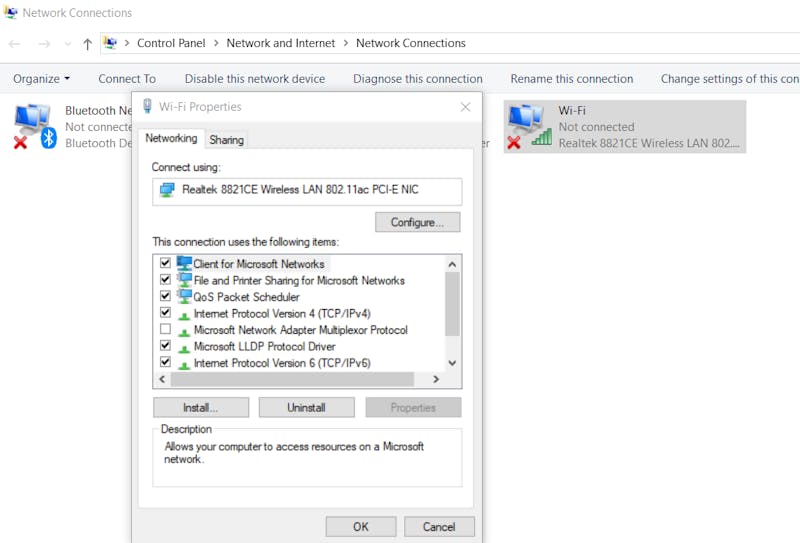
- On a Windows 8/8.1/10 PC, you can easily check Wi-Fi adapters properties by navigating to “Control Panel\Network and Internet\Network Connections”, right-clicking your adapter, and selecting "Properties".
#5: Reduce Wi-Fi Traffic on Your Network
Pro Tips
- Is your neighbor using your Wi-Fi bandwidth? You should use a strong Wi-Fi password and secure protocol like WPA2 to secure your Wi-Fi network. This will help reduce the likelihood of “unwanted guests” connecting.
- If you are operating a business network, create a separate Wi-Fi network for guests. This offers security benefits too. It will help you keep business-critical traffic and guest traffic isolated.
#6: Change Your Wi-Fi Channel or Frequency
If you are in an area with many Wi-Fi devices and networks, this can lead to a lot of interference that degrades your Wi-Fi performance. This is because there are a limited number of Wi-Fi channels you can send data across. In high-traffic areas, like office buildings or apartment complexes, different networks can overlap with one another. If you change your Wi-Fi channel or frequency, you may be able to avoid some of the interference and improve your Wi-Fi performance.
Pro Tips
- With 2.4 GHz connections in North America, channels 1, 6, and 11 do not overlap. Using a non-overlapping channel is a good idea. 6 is a standard default, so that you may have better luck with 1 or 11.
- 5 GHz connections offer more channels than 2.4 GHz and aren’t as congested with traffic from other consumer electronics. However, 2.4 GHz signals can travel farther and are better at penetrating through solid objects. Keep these tradeoffs in mind when selecting Wi-Fi frequencies.
- Wi-Fi network analyzer software can help advanced users identify noisy Wi-Fi channels.
#7: Update Your Wi-Fi Router Firmware
Pro Tips
- Release notes and upgrade instructions are your friend! Be sure to read them before performing a router firmware update.
- Unless you are an advanced user with a specific purpose, only use router firmware from the manufacturer. If you are an advanced user with a specific purpose, check out tip #12 😉.
#8: Strategically add wireless access points (WAPs)
Pro Tip
- WAPs are useful when you want to extend Wi-Fi signal but can’t afford the added latency common with signal boosters.
#9: Use Wi-Fi QoS

Quality of Service or QoS allows you to prioritize some traffic over others. QoS settings are configured at your Wi-Fi source (usually a Wi-Fi router). Setting QoS rules allow you to ensure your most critical applications are prioritized when data is sent over your Wi-Fi network. For example, if you are a gamer, you may want to prioritize traffic for your favorite games over all other traffic. Similarly, a business may wish to give the highest priority to VoIP (Voice over IP) calls.
Pro Tips
- QoS doesn’t increase your bandwidth or speed, it simply ensures high-priority traffic is sent first. This can improve Wi-Fi performance for specific apps and services.
- Not all Wi-Fi routers support QoS. Among those that do, specific QoS functionality varies significantly. Check with the manufacturer for specifics on QoS before making a purchase.
#10: Remove Obstructions to Your Wi-Fi Signal

Wi-Fi signals are simply radio waves. This means they have to pass through the air to enable communication. The more obstructions there are between a Wi-Fi source and a Wi-Fi client, the worse performance can become. Conversely, the more obstructions you remove, the more you can improve performance.
Pro Tip
- Physical obstructions (e.g. brick or cement walls), reflective surfaces (e.g. mirrors), and radio interference are 3 common causes of Wi-Fi performance degradation. You should keep this in mind when positioning your Wi-Fi source and look to remove them as much as practical.
#11: Use Stronger Wi-Fi Antennas

Since Wi-Fi is based on radio waves, it makes sense that it involves antennas. Of course, as you can tell by simply looking at many Wi-Fi devices, not all of them support aftermarket upgrades to their antenna. However, for those that do, an antenna upgrade can be a fairly quick and inexpensive way to boost your Wi-Fi performance.
Pro Tips
- Use an omnidirectional antenna to increase the Wi-Fi signal in all directions.
- Use a directional Wi-Fi antenna to increase the Wi-Fi signal in a specific direction.
- Wi-Fi antenna power is measured in decibels or dB (sometimes listed as dBi). While there are a number of variables that impact performance, a higher decibel rating implies a stronger antenna.
#12: (Advanced users!) Use 3rd party Wi-Fi firmware
Warning: 3rd party firmware can potentially render your Wi-Fi router unusable.

If you’re comfortable with the risks, there are plenty of potential upsides to installing 3rd party open source router firmware like OpenWrt or DD-Wrt. One of the upsides is possibly improving your Wi-Fi performance. For example, a 3rd party router firmware may enable you to increase transmit power or unlock other features. Of course, the risk of operating the router outside of manufacturer recommendations should be considered before using a 3rd party firmware. For example, in the increased transmit power example, there is the related risk of burning out the transmitter.
Closing Thoughts
There are many ways to improve Wi-Fi performance. Choose the tips that work for you!
As we have seen, there are many ways you can boost your Wi-Fi performance. However, there is no magic bullet that will serve as a cure-all for your Wi-Fi performance challenges. You’ll need to evaluate your existing hardware and environment and decide which tips work best for you.